New Delhi, Feb 12 (PTI) In a landmark judgement that delivered a big blow to the government, the Supreme Court on Thursday annulled the electoral bonds scheme for political funding, saying it violates the Constitutional right to freedom of speech and expression as well as the right to information.
In its verdict months ahead of the Lok Sabha polls, the apex court ordered the State Bank of India (SBI) to disclose to the Election Commission the names of the contributors to the six-year-old scheme.
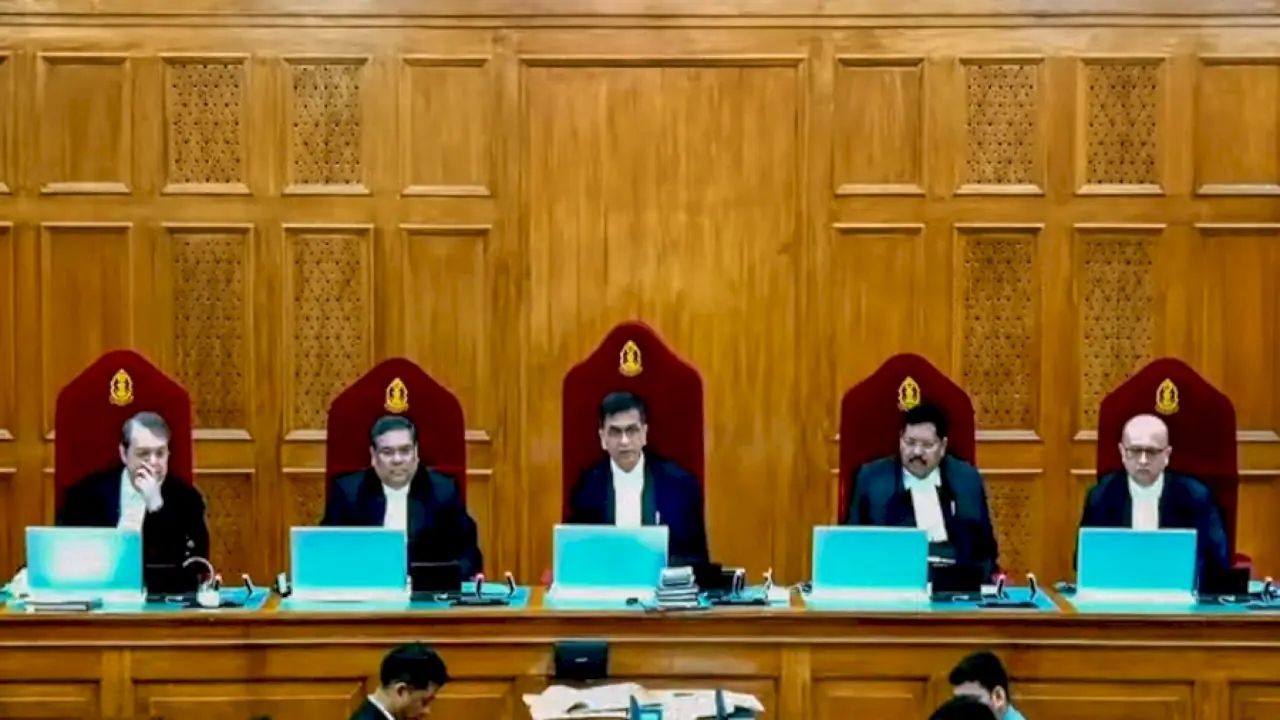
A five-judge Constitution bench headed by Chief Justice D Y Chandrachud directed that the SBI must disclose details of each electoral bond encashed by political parties. The information should include the date of encashment and the denomination of the bonds and be submitted to the poll panel by March 6.
The Election Commission should publish the information shared by SBI on its official website by March 13, the bench said.
The bench, also comprising Justices Sanjiv Khanna, B R Gavai, J B Pardiwala and Manoj Misra, delivered two separate and unanimous verdicts on the pleas challenging the scheme.
Pronouncing the verdict, the CJI said the scheme is violative of the right to freedom of speech and expression under Article 19(1)(a) of Constitution.
“The electoral bonds scheme and the impugned provisions to the extent that they infringe upon the right to information of the voter by anonymising contribution through electoral bonds are violative of Article 19 (1)(a),” the CJI said while pronouncing the verdict.
The bench said the fundamental right to privacy also includes the citizens’ right to political privacy and affiliation.
It also held as invalid the amendments made in various laws, including the Representation of Peoples Act and the Income Tax laws.
The apex court directed that the SBI shall stop issuing electoral bonds and submit details of bonds purchased since April 12, 2019 till date to the Election Commission. It should also submit details of political parties which have received contributions through electoral bonds since April 12, 2019 till date to the poll panel.
“This will restore people’s faith in democracy. This is the greatest thing that could have happened. This is the most historic judgement that we have got from the Supreme Court in the last five-seven years. It is a great boon for democracy,” former chief election commissioner S Y Quraishi told PTI Videos.
“Electoral Bonds declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court. Three cheers for the SC!” he added in a post on X.
In October last year, the bench began hearing arguments on the four petitions, including those filed by Congress leader Jaya Thakur, the Communist Party of India (Marxist) and the NGO Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR).
“Those who were donating money through electoral bonds were not disclosing their names. Somewhere they would want favours from the government… This verdict will make a difference. It will protect the interest of people,” Thakur told PTI Videos after the verdict.
Advocate Varun Thakur, who represented Thakur in the case, described the verdict as a setback for the government “because from 2018 to 2024 whatever transactions which have taken place have to be made public”.
“It is a setback because of the way anonymous contributions were received through the scheme. Now accountability will be fixed. It is a historical step for democracy and today, we can say democracy has won,” Thakur added.
“The Supreme Court has directed the SBI to furnish complete information about who purchased the bonds, who encashed the bonds… All this information will have to be submitted to the Election Commission, which will have to display it on its website so that the people come to know who purchased the bonds,” advocate Prashant Bhushan, who represented ADR, said.
The scheme, which was notified by the government on January 2, 2018, was pitched as an alternative to cash donations made to political parties as part of efforts to bring transparency in political funding.
According to the provisions of the scheme, electoral bonds may be purchased by any citizen of India or entity incorporated or established in the country. An individual can buy electoral bonds, either singly or jointly with other individuals without disclosing the identity.
Critics have said this eliminates transparency in electoral funding and gives an edge to ruling parties.
On November 2 last year, the top court reserved its verdict in the matter.
In April 2019, the apex court declined to stay the scheme and made it clear that it would accord an in-depth hearing on the pleas as the Centre and the Election Commission had raised “weighty issues” that had “tremendous bearing on the sanctity of the electoral process in the country”.