New Delhi, Oct 28, 2023: Diabetes is a leading threat to public health globally, and the view is gloomier for countries like India, where the diabetes burden has risen significantly in recent decades and will continue to rise in the coming decades.
As the prevalence of diabetes rises, more young adults and adolescents tend to develop diabetes, particularly if they are overweight/obese.
Not just this, more people are now falling prey to borderline diabetes. It is a condition wherein blood sugar levels are slightly above the normal range, but not high enough to be called diabetes. A report published in 2018 estimated 1 in every 6 Indians to have borderline diabetes.
what is HbA1c?
HbA1c is your average blood glucose (sugar) levels for the last two to three months. If you have diabetes, an ideal HbA1c level is 6.5% or below that means estimated average blood glucose 154 mg/dL.
If you’re at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, your target HbA1c level should be below 6% that means estimated average blood glucose 126 mg/dL.
What does HbA1c mean?
HbA1c is what’s known as glycated haemoglobin. This is something that’s made when the glucose (sugar) in your body sticks to your red blood cells. Your body can’t use the sugar properly, so more of it sticks to your blood cells and builds up in your blood. Red blood cells are active for around 2-3 months, which is why the reading is taken quarterly.
A high HbA1c means you have too much sugar in your blood. This means you’re more likely to develop diabetes complications, like serious problems with your eyes and feet.
Knowing your HbA1c level and what you can do to lower it will help you reduce your risk of devastating complications. This means getting your HbA1c checked regularly. It’s a vital check and part of your annual review. You’re entitled to get this test at least once a year. But if your HbA1c is high or needs a little more attention, it’ll be done every three to six months. It’s really important not to skip these tests, so if you haven’t had one in over a year contact your healthcare team.
Once you know your HbA1c level, it’s important that you understand what the results mean and how to stop them from getting too high. Even a slightly raised HbA1c level makes you more at risk of serious complications, so get all the facts here and be in the know about HbA1c.
What is a HbA1c test?
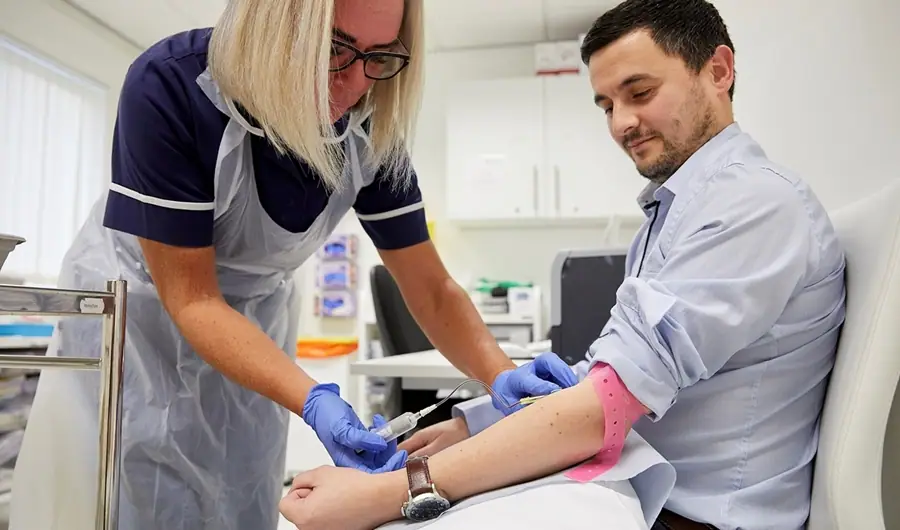
The hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test measures the amount of blood sugar (glucose) attached to your hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the part of your red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. It is an important blood test that gives a good indication of how well your diabetes is being controlled.
You can check these average blood sugar levels yourself, but you’ll have to buy a kit, whereas your healthcare professional will do it for free. It’s different from a finger-prick test, which is a snapshot of your blood sugar levels at a particular time, on a particular day.
You find out your HbA1c level by getting a blood test by a doctor or nurse. Your healthcare team will arrange this for you, but chase it up with your GP if you haven’t had one for a few months.
Most people will have the test every three to six months. But you may need it more often if you’re planning for a baby, your treatment has recently changed, or you’re having problems managing your blood sugar levels.
And some people will need the test less often, usually later on during pregnancy. Or need a different test altogether, like with some types of anaemia. A fructosamine test can be used instead, but it’s very rare.
An HbA1c test is also used to diagnose diabetes, and to keep an eye on your levels if you’re at risk of developing diabetes (you have prediabetes).
The test is sometimes called haemoglobin A1c or just A1c.
Your HbA1c results
You should get the results quickly. The result of the HbA1c test lets your healthcare team know if they need to change your treatment or medication to help you manage your levels better. But it also tells you a number and it’s important you understand what this means. Some people find it helps to write their results down in a diary, to keep track of them and see if they can spot any trends.
And your HbA1c can change for lots of reasons, including:
- if you’re unwell
- if you’re taking other medicines, like steroids
- changes in lifestyle
- if you’re feeling very stressed or you’re depressed.
You’ll talk to your healthcare team about a target level that you need to aim for. We know this isn’t as easy as it sounds, but it’s important you do everything you can to keep in your target range. The longer your HbA1c level is even slightly high, the more you’re at risk of developing life-threatening complications.
What is a normal range for an HbA1c test?
HbA1c below 5.7% is normal, between 5.7 and 6.4% indicates you have prediabetes, and 6.5% or higher indicates you have diabetes.
HbA1c levels and targets
But everyone’s different. So your healthcare team may give you an individual target level that takes into account your current level and when your next test is. So you can bring it down in stages and isn’t a sudden big drop.
And we’re not saying it’s easy to get to and stay at this level. We know it’s difficult but you can succeed.
How to lower your HbA1c levels
If your levels have gone above your target since your last check, it’s understandable to be worried. Even a slightly high HbA1c level puts you more at risk of developing serious complications in your body. But knowing your numbers and what that means is an important and good first step – now you need to know how to lower them.
Lots of things can cause your HbA1c levels to change and there’s action you and your healthcare team can take to bring them down to your target level:
- Your diabetes team may need to review your medication and increase the dose or try a new one.
- Ask them about local diabetes education courses – there’s always more to learn with diabetes and a course will help you take practical steps to lower your HbA1c.
- Get more active – moving more is good for everyone, but it can specifically help to bring down your HbA1c levels.
- Get advice on balanced, healthy eating.
- Stop smoking – smoking makes it harder for blood to flow around your body.
Lots of things can cause your HbA1c levels to change and there’s action you and your healthcare team can take to bring them down to your target level.
Finger-prick tests
There are following three Types of finger-prick tests.
Fasting Blood Sugar Test
This measures your blood sugar after an overnight fast (not eating). A fasting blood sugar level of 99 mg/dL or lower is normal, 100 to 125 mg/dL indicates you have prediabetes, and 126 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes.
Glucose Tolerance Test
This measures your blood sugar before and after you drink a liquid that contains glucose. You’ll fast (not eat) overnight before the test and have your blood drawn to determine your fasting blood sugar level. Then you’ll drink the liquid and have your blood sugar level checked 1 hour, 2 hours, and possibly 3 hours afterward. At 2 hours, a blood sugar level of 140 mg/dL or lower is considered normal, 140 to 199 mg/dL indicates you have prediabetes, and 200 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes.
Random Blood Sugar Test
This measures your blood sugar at the time you’re tested. You can take this test at any time and don’t need to fast (not eat) first. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes.
HbA1c test and finger-prick test – what’s the difference?
Inputs with Diabetes UK